Frequently Asked Questions
Using Multiple Compilation Units
In order to create a project using multiple compilation units, one of the following IDE versions of the CCS C Compiler needs to be used: PCW, PCWH, PCWHD, PCDIDE.
Traditionally, the CCS C Compiler uses only one compilation unit and multiple files are implemented using #INCLUDE. When using multiple compilation units, care must be given that pre-processor commands which control the compilation are compatible across all units. It is recommended that directives such as #FUSES, #USE, and the device header file are all put in a single file included by all units. When a unit is compiled, it will output a relocatable object file (*.o) and symbol file (*.osym).
The following is an example overview of using multiple compilation units. Refer to MCU.zip in the examples directory or download the file from the CCS website here.
| Files Included in Project Example | |
|---|---|
| File | Purpose |
| main.c | Primary file for the first compilation unit. |
| filter.c | Primary file for the second compilation unit. |
| report.c | Primary file for the third compilation unit. |
| project.h | Header file with project wide definitions included by all units. |
| filter.h | Header file with external definitions for filter.c included by all units that use filter.c functions. |
| report.h | Header file with external definitions for report.c included by all units that use report.c functions. |
| project.c | File used to import list of units in the project for linker.bat. |
| project.pjt | Project file used to list the units in the project for build.bat. |
| build.bat | Batch file that compiles units which need to be compiled and linked. |
| buildall.bat | Batch file that compiles and links all units. |
| linker.bat | Batch file that compiles and links all units using a script. |
| File Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| main.c | filter.c | report.c | |
| #INCLUDE |
project.h filter.h report.h |
project.h report.h |
project.h |
| Definitions |
main( ) |
clear_data( ) filter_data( ) |
report_data_line( ) report_line_number( ) report_error( ) |
| Uses |
clear_data( ) filter_data( ) report_data_line( ) report_line_number( ) |
report_error( ) |
|
| Compilation Files | |
|---|---|
| File | Purpose |
| *.o | Relocatable object file generated by each unit. |
| *.err | Error file generated by each unit. |
| *.osym | Unit symbol file generated by each unit. |
| project.hex | Program image generated for the project. |
| project.lst | C and ASM listing file generated for the project. |
| project.sym | Project symbols file generated for the project. |
| project.cof | Debugger file generated for the project. |
Select the applicable option below being used to compile the project:
- Using Command Line to Build a Project
- Using Command Line to Re-Build Changed Files in a Project
- Using a Linker Script
- Using the CCS PCW IDE
- Using the MPLAB IDE
- Additional Notes
Using Command Line to Build a Project
- Move all of the source files for the project into a single directory.
- Using a text editor, create the file buildall.bat based off of the following example in order to compile the files and build the project.
- The path should point to the CCSC.exe file in the CCS C Compiler installation directory.
- Add any additional compiler options.
- Use the EXPORT option to include the necessary *.c files.
- Use the LINK option to generate a *.hex file.
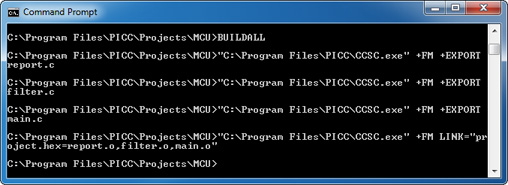
- Double-click on the buildall.bat file or use a command prompt with the command BUILDALL to build the project using all of the files.
"C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM +EXPORT report.c "C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM +EXPORT filter.c "C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM +EXPORT main.c "C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM LINK="project.hex=report.o,filter.o,main.o"
Follow these guidelines when creating a file to compile and build your own project:
Using Command Line to Re-Build Changed Files in a Project
- Using a text editor, create the file project.pjt based off of the following example in order to include the files that need to be linked for the project.
- Using a text editor, create the file build.bat based off of the following example in order to compile only the files that changed and re-build the project.
- The path should point to the CCSC.exe file in the CCS C Compiler installation directory.
- Add any additional compiler options.
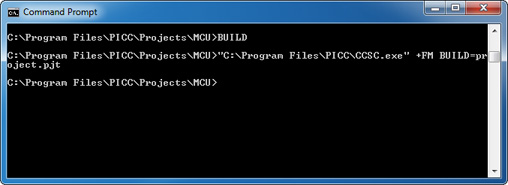
- Use the BUILD option to specify the *.pjt file.
- Double-click on the build.bat file or use a command prompt with the command BUILD to re-build the project using only the files that changed.
[Units] Count=3 1=report.o 2=filter.o 3=main.o Link=1
"C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM BUILD=project.pjt
Follow these guidelines when creating a file to compile and build your own project:
Using a Linker Script
- Using a text editor, create the file project.c based off of the following example in order to include the files that need to be linked for the project.
- Using a text editor, create the file linker.bat based off of the following example in order to compile the files and build the project.
"C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM +EXPORT report.c "C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM +EXPORT filter.c "C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM +EXPORT main.c "C:\Program Files\PICC\CCSC.exe" +FM project.c
Follow these guidelines when creating a file to compile and build your own project:
- The path should point to the CCSC.exe file in the CCS C Compiler installation directory.
- Add any additional compiler options.
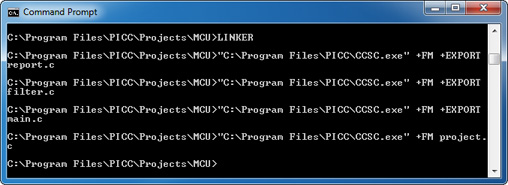
- Use the EXPORT option to include the necessary *.c files.
- Double-click on the linker.bat file or use a command prompt with the command LINKER to build the project using all of the files.
#import(FILE=report.o) #import(FILE=filter.o) #import(FILE=main.o)
Using the CCS PCW IDE
- Open the CCS PCW IDE and select File -> New -> Create Project from the ribbon along the top of the main window or from the menu bar if using the classic style IDE. In the file section prompt that appears, select the main source file of the project.
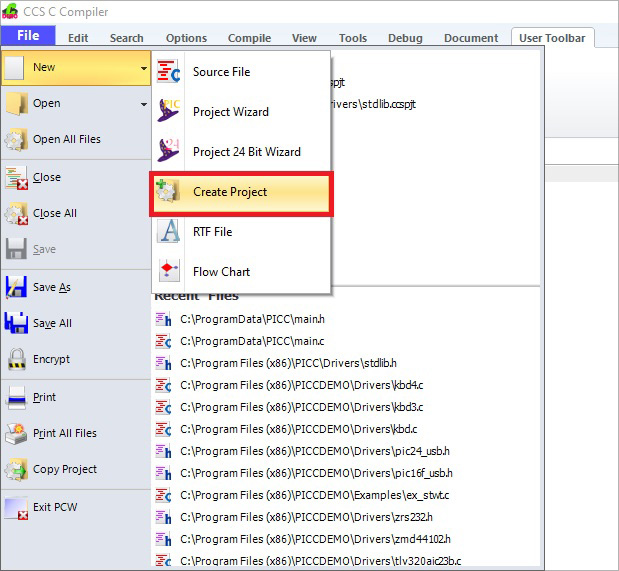
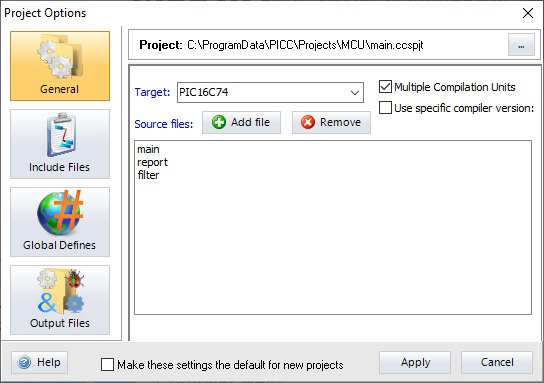
- When the Project Options window appears, select the type of chip being used in the project. Check the box next to the option Multiple Compilation Units; this will allow additional source files to be added. Click the + Add file button and select the other source files used in the project. Click the Apply button to create the project.
- To compile the files and build the project, select Compile from the ribbon along the top of the main window, or from the menu bar if using the classic style IDE, and select one of the following options:
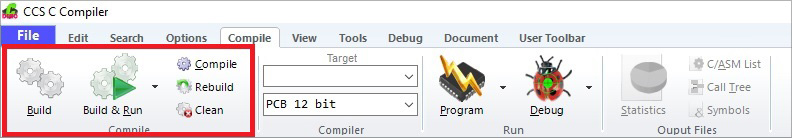
| Compilation Options | |
|---|---|
| Options | Purpose |
| Build | Compiles units that have changed since the last compilation and rebuilds the project. |
| Build and Run | Performs a build and then programs the image to the microcontroller using the selected programming tool. The microcontroller then runs the new program. |
| Compile | Compiles the current unit. |
| Rebuild | Compiles all the units and builds the project. |
| Clean | Deletes the output files for the project. |
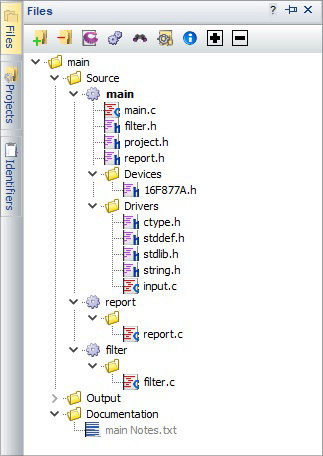
- After a project has been compiled, the files used during the compilation will appear under the unit's name in the Files pane.
Using the MPLAB IDE
- Open the MPLAB IDE and select Project -> New... from the menu bar along the top. In the prompt that appears, select the main source file of the project.
- Select Project -> Select Language Toolsuite... from the menu bar along the top. In the window that appears, select the CCS C Compiler from the drop-down list in the Active Toolsuite: field. Make sure the correct directory location is displayed for the compiler.
- Select Configure -> Select Device... from the menu bar along the top. In the window that appears, select the correct PIC® MCU or PIC® DSC from the list provided.
- Add source files to the project by either selecting Project -> Add Files to Project... from the menu bar along the top or by right-clicking on the Source Files folder in the project window and selecting Add Files... in the pop-up menu. In the prompt that appears, select the source files to add to the project.
- Select Project -> Build Options... from the menu bar along the top. The window that appears will allow changes to be made to the output directory, include directories, output files generated, etc. for the entire project or just individual units.
- To compile the files in a project and build the project itself, select Project from the menu bar along the top, or right-click on the files in the Project window and select one of the following options:
| Compilation Options | |
|---|---|
| Options | Purpose |
| Compile | Compiles the selected unit and will not re-link the project after compilation. |
| Make | Compiles units that have changed since the last compilation and rebuilds the project. |
| Build All | Compiles all the units, deletes intermediate files, and builds the project. |
| Clean | Deletes the output files for the project. |
- If there is only one source file in the project, it will be compiled and linked in a single step without creating a *.o file. A *.o file that has already been compiled can be added to the project and linked during the make / build process.
NOTE:
Additional Notes
- To make a variable or function private to a single unit, use the static keyword. By default, variables declared outside a function at the unit level are visible to all other units in the project. If the static keyword is used on a function or variable that is accessed outside of the local unit, a link time error will occur.
- If two units have a function or a unit level variable of the same name, an error will occur unless one of the following conditions is true:
- The identifier is qualified with the keyword static.
- The argument list is different for both functions, allowing them to co-exist according to normal overload rules.
- The contents of the functions are identical, such as when the same *.h file is included in multiple files. The linker will then delete the duplicate functions.
- For a project with multiple compilation units, it is best to include a file such as project.h which includes the #INCLUDES, #DEFINES, pre-processor directives, and any other compiler settings that are the same for all the units in a project.
- When a setting such as a pre-processor directive is included in the main header file shared between units, a library is created in each of the units. The linker is able to determine that the libraries are duplicates and removes them during the final linking process.
- When building a project, each unit being used in the project has its own error file. When using a *.bat file to do the unit compilations, it may be useful to terminate the process on the first error. Using the +CC command line option, the compiler will return an error code if the compilation fails.
For additional help using multiple compilation units, contact CCS Technical Support.